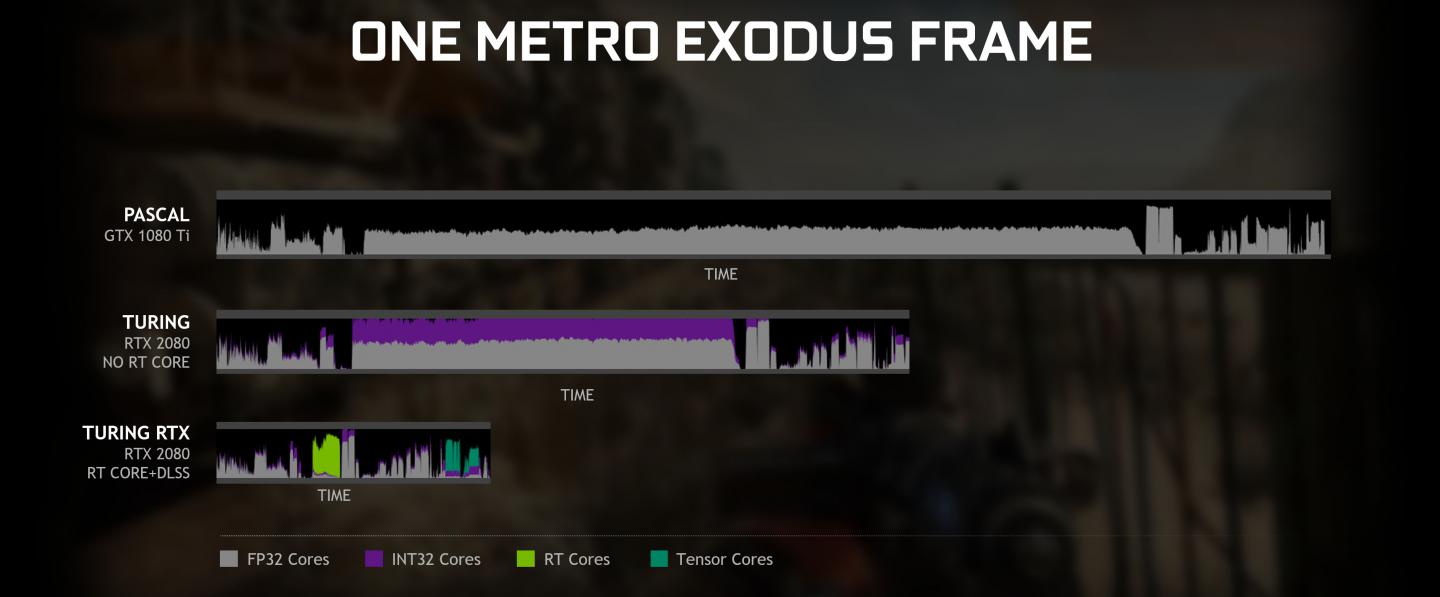
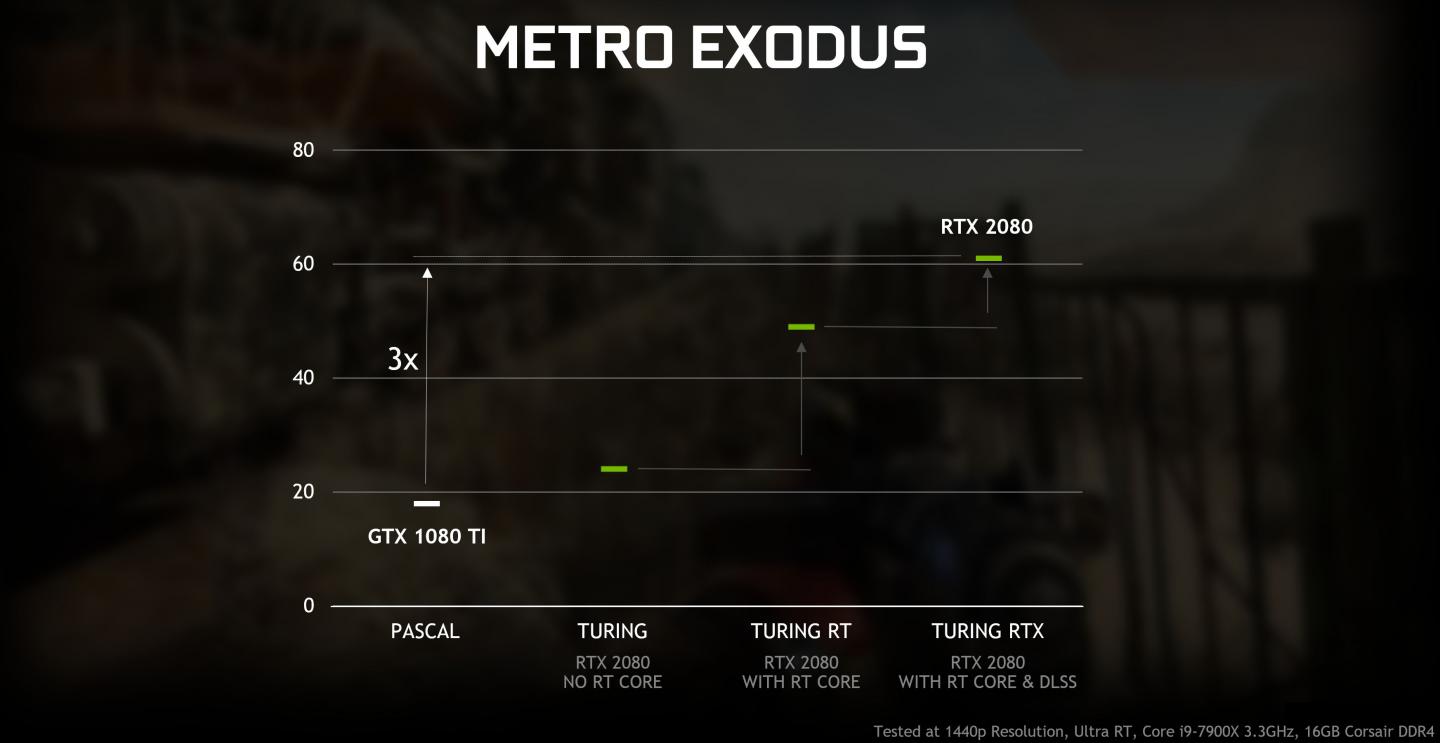
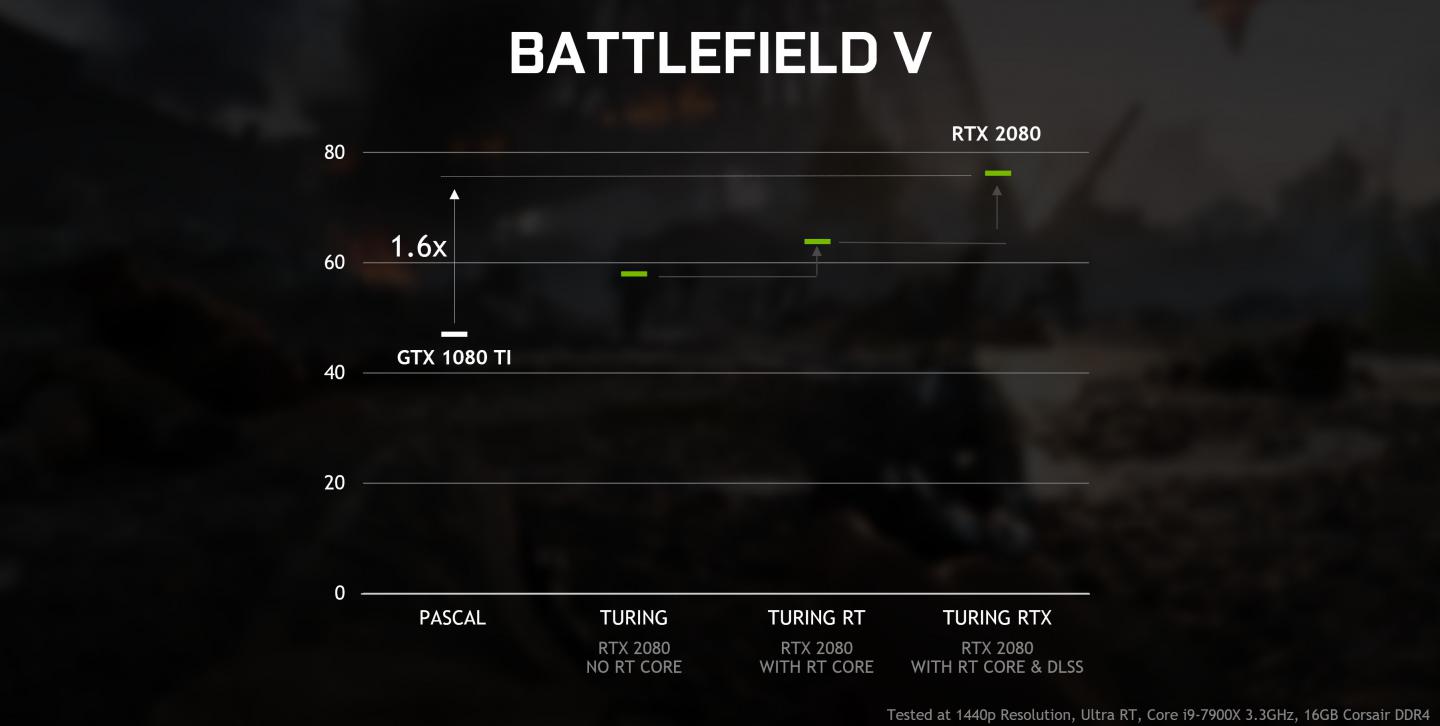
Nvidia announced that it will bring support for Microsoft's DXR-API (the API responsible for real-time ray tracing), to older GPUs. This invokes the 10-series and recently introduced 16-series GPUs series.
The new driver thus makes it possible to use real-time raytracing in games via DXR as part of DirectX 12 without exclusive RT cores and thus on the traditional computing cores. However, with DXR effects enabled, performance will be significantly lower than Turing's counterparts with specialized RT cores - so the purpose remains to be seen. Also AMD could use DXR on its Radeon graphics cards, if supported by the driver. AMD has not yet released an official raytracing driver.
A new GeForce driver is due to be released in April, that one will add the compatibility. The Titan X, Titan V and Titan XP would also get supported. It is good to note that laptops with similar GPUs may also expect to get DX-R with the new driver, including the more economical Max-Q versions. Performance can be disappointing, NVIDIA mentions. Only very basic raytracing effects would work.
DLSS remains exclusively for Turing RTX
From now on Raytracing will no longer be available exclusively on GeForce RTX at Nvidia. But with DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) it is different. The alternative AI-based antialiasing will continue to be provided only with the dedicated tensor cores of the RTX family, Nvidia said in the Q & A after the GDC presentation to media representatives.
At least theoretically, it would be possible to create a counterpart to the proprietary DLSS via the Microsoft API Windows Machine Learning (WinML) or DirectML. DirectML takes advantage of the unified compute units of GPUs, with which even Radeon graphics cards from AMD could offer such a function, as an AMD employee had already suggested in an interview.
So in short, people can enable DirectX Raytracing ( DXR ) on GeForce GTX 1060 6GB and higher graphics cards via a Game Ready Driver update, expected in April. DLSS, no bueno.
supported GPUs