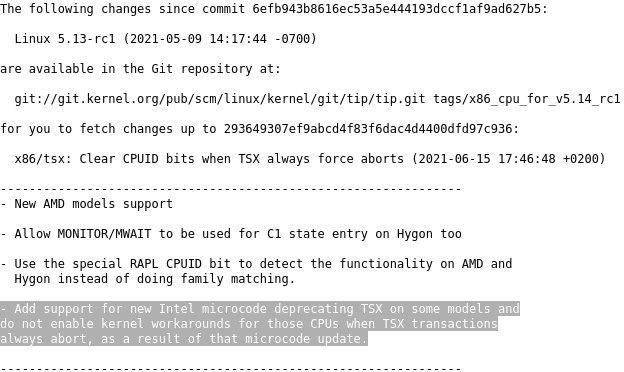
Intel has decided to deactivate Transactional Sync Extensions in Skylake, Kaby Lake, Coffee Lake and Whiskey Lake processor chips. Intel deactivates the feature because of memory ordening errors and .. hackers can exploit it.
New kernel patches will disable TSX in a micro-update for the CPU soon. Deactivating TSX in some tasks will result in lower performance in older chips.TSX adds hardware transactional memory support to the CPUs, giving them up to 40 percent better performance in certain tasks. TSX has been in chips based on the Haswell microarchitecture since the Skylake generation in 2013.
In 2016, it was discovered that TSX could be exploited for a side-channel timing attack, where hackers could break kernal address space layout randomization, or KASLR, to gain access to a system. That's one of the reasons the feature is no longer supported.
TSX also can cause an error in the memory ordering, i.e. the sequence of accessing memory. At the beginning of this month, Intel published a white paper. This is known as a problem since 2018 and is disabled with SGX and SMM. With the micro-update, TSX can no longer be accessed and there is no workaround in the Linux kernel.
Intel to disable insecure TSX feature on older CPUs