SSD Performance Read and Write performance (linear) analysis
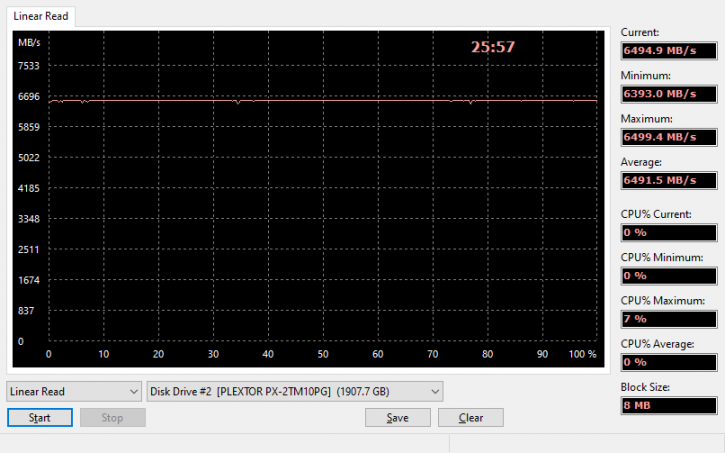
SSD Performance Linear Read and Write performance analysis
In this chapter of the review, we will completely fill the SSD with data and observe what happens to the write performance as a result of doing so. So, for example, if the SSD has a capacity of 2TB, we'll read and then write continually. So we can see how the SSD would react when subjected to large amounts of read and write activities at the same time.
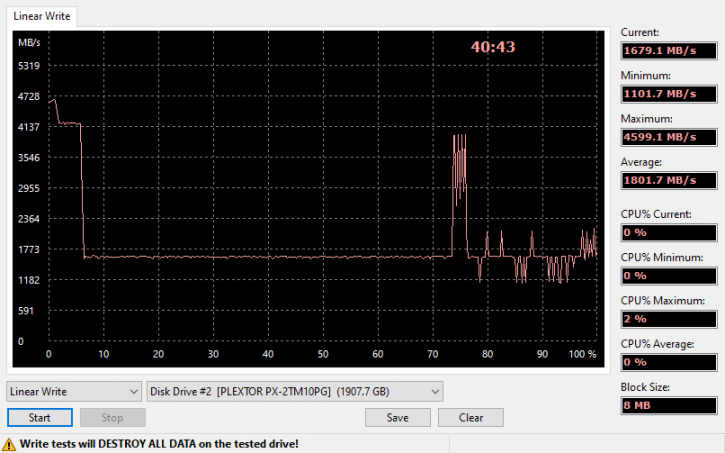
As a solution to the sluggish read/write performance of TLC SSDs, manufacturers have added an SLC cache, sometimes known as a pSLC cache, into their products (pseudo). The amount of space available is determined by the capacity of the SSD. If there is still some free SLC cache space available, the SSD's read/write performance is comparable to that of SLC NAND, as long as the space has not been totally utilized. When the SLC cache is completely depleted, the firmware (FW) initiates background garbage collection in order to clear off the remaining space. Additionally, while garbage collection is taking place, data is still being sent to the drive, which has an adverse effect on its overall performance. With this test, we can examine what happens when the cache fills up and the write speed falls back to the lowest feasible value.
We can observe that read performance is a constant, we average out at 6492 MB/sec throughout reading the entire disk capacity, impressive.
Above linear write testing. Here we write a full 2 terabytes of SSD capacity. And on any MLC/TLC/QLC NAND storage drive, the dreaded Achilles heel comes into play - once that pSLC buffer runs dry, you're back to raw TLC write performance. Averaged out in writing data linear (2TB writes!) we still end up at an average of 1800 MB/sec. Mind you that for the first 7% of the SSD, writes remain close to 143 GB of writes. However, the peak value drops after roughly 50 GB which is the depleted pSLC cache.