Hardware installation - Power consumption
Hardware installation
Installation of any of GeForce graphics cards is really easy. Once the card is installed and seated into the PC, we connect the two 8-pin PEG power connectors to the graphics card.
Each connector delivers up-to roughly 150W. Combined with another 75W over the PCIe bus you are looking at roughly 375 Watt that the graphics card can use. Preferably your power supply is compatible; most high-end PSUs built after the year 2008 have these connectors as standard.

Preferably the PEG headers should come directly from the power supply and are not converted from 4-pin Molex and 6-pin peripheral connectors. Don't forget to connect your monitor, you can now turn on your PC, boot into Windows, install the latest compatible NVIDIA GeForce Forceware driver and after a reboot all should be working. No further configuration is required or needed.
Power Consumption
Let's have a look at how much power draw we measure with this graphics card installed.
The methodology: We have a device constantly monitoring the power draw from the PC. We simply stress the GPU, not the processor. The before and after wattage will tell us roughly how much power a graphics card is consuming under load.
Note: We decided to move away from Furmark / OCCTGPU in early 2011 and are now using a game like application which stresses the GPU 100% yet is much more representable of power consumption and heat levels coming from the GPU. We however are not disclosing which application that is as we do not want INTEL/AMD/ATI/NVIDIA to "optimize & monitor" our stress test whatsoever, for our objective reasons of course.
Our test system is based on a power hungry Core i7 965 / X58 system. This setup is overclocked to 3.75 GHz. Next to that we have energy saving functions disabled for this motherboard and processor (to ensure consistent benchmark results). On average we are using roughly 50 to 100 Watts more than a standard PC due to higher CPU clock settings, water-cooling, additional cold cathode lights etc.
We'll be calculating the GPU power consumption here, not the total PC power consumption.
Measured power consumption
- System in IDLE = 138 W
- System Wattage with GPU in FULL Stress = 302 W
- Difference (GPU load) = 164 W
- Add average IDLE wattage ~10 W
- Subjective obtained GPU power consumption = ~ 174 Watts
Mind you that the system wattage is measured at the wall socket side and there are other variables like PSU power efficiency. So this is a calculated value, albeit a very good one.
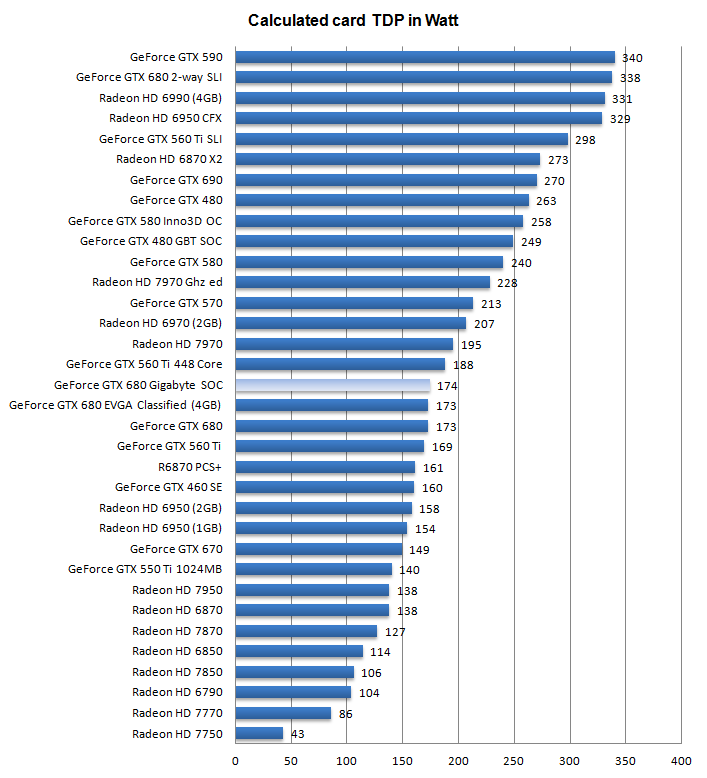
Above, a chart of relative power consumption. Again the Wattage shown is the card with the GPU(s) stressed 100%, showing only the peak GPU power draw, not the power consumption of the entire PC and not the average gaming power consumption.
Here is Guru3D's power supply recommendation:
- GeForce GTX 680 - On your average system the card requires you to have a 550 Watt power supply unit.
- GeForce GTX 680 SLI - On your average system the cards require you to have a 750 Watt power supply unit as minimum.
If you are going to overclock GPU or processor, then we do recommend you purchase something with some more stamina.
There are many good PSUs out there, please do have a look at our many PSU reviews as we have loads of recommended PSUs for you to check out in there. What would happen if your PSU can't cope with the load:
- bad 3D performance
- crashing games
- spontaneous reset or imminent shutdown of the PC
- freezing during gameplay
- PSU overload can cause it to break down
Let's move to the next page where we'll look into GPU heat levels and noise levels coming from this graphics card.

