Power Consumption and Temperatures
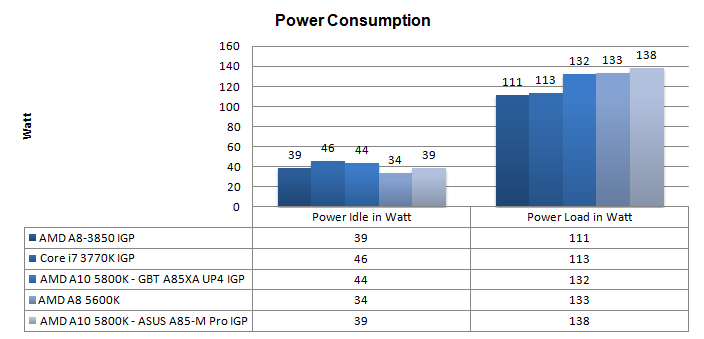
Power Consumption
Power consumption wise, AMD was able to keep the TDP of these APUs on track, either 60W or 100W depending on your choice of APU. A higher power draw would result in unhappy customers, but obviously also could endanger heat levels.
The APU is a pretty clever product when it comes to its power design and power states. Not only can the processor cores independently be throttled down, lowering voltage and what not, there are different power states inside the APU allowing nearly complete shutdown of segments/domains within the APU. For example, if the GPU is not used, it can be powered or slowed down. The same goes for CPU cores.
We ran the AMD APU both with and without a dedicated graphics card. Without one (using the internal IGP) the PC idles at only 44 Watts. When we place load on the CPU and we see the power draw rise the system now consumes roughly 132 Watts. This is with merely an SSD and 8GB memory installed. Your average PC will draw a little more power if you add optical drives, HDDs, soundcards etc.
I want to make it very clear that power consumption measurements will differ per PC and setup. Your attached components use power but your motherboard can have additional ICs installed like audio controller, LUCID chips, network controllers, extra SATA controllers, extra USB controllers, and so on. These parts all consume power.
Under stress with a decent heatpipe cooler you are looking at 40 to 50 Degrees C on the APU. No problem.