Power Consumption and temperatures
Sandy Bridge Power Consumption & Temperatures
Here's where we'll slowly move into actually testing the processors and respective chipsets.
The new Sandy Bridge based processors are a bit of a redesign alright and as a result they are quite energy friendly processors. What you'll notice a lot is that in idle these things kick ass in matters of power consumption, whereas at peak TDP they behave quite normally.
 How we measure power consumption
How we measure power consumption
A processor like the Core i5 2500K for example consumes only 106 Watts, and that is with all cores stressed, and that's including a reference H67 chipset, one solid state drive, the memory and active cooler, no dedicated graphics card. Once that processor goes into an IDLE state (and again -- without a dedicated graphics card) we measure merely below 40 Watts IDLE power consumption. And that's just crazy.
Unfortunately, once you insert a dedicated graphics card things change quickly. When we add a GeForce GTX 580 for example that IDLE power consumption typically jumps upwards to roughly 60~70 Watts with a wattage peak of 130 to 140W with the four processor cores stressed. That's still really good though.
The ECS demands a little more power though, this is due to the extra integration of ICs like the Hydra chip, extra USB 3 controller and extra SATA controller.
- We average out at roughly 88W idle (with a GeForce GTX 580 - 8GB Memory and one SSD installed).
- Once we stress the CPU cores overall power consumption went up towards 169W
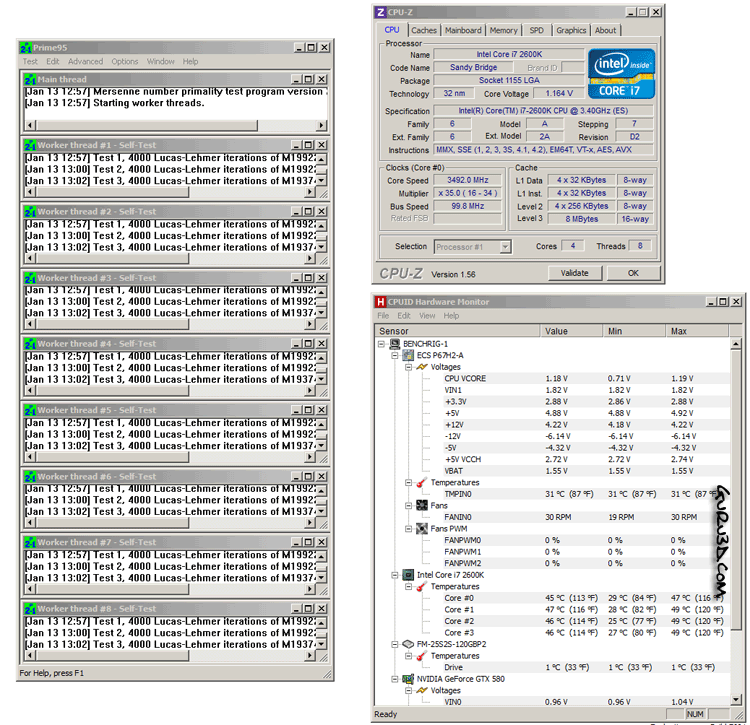
Temperature wise, both the 2500 and 2600 processors are roughly the same. The results above are based on the motherboards, reference clock frequencies and the reference stock Intel CPU cooler. Per core temps will peak to roughly 50 Degrees C with the Intel stock cooler.
