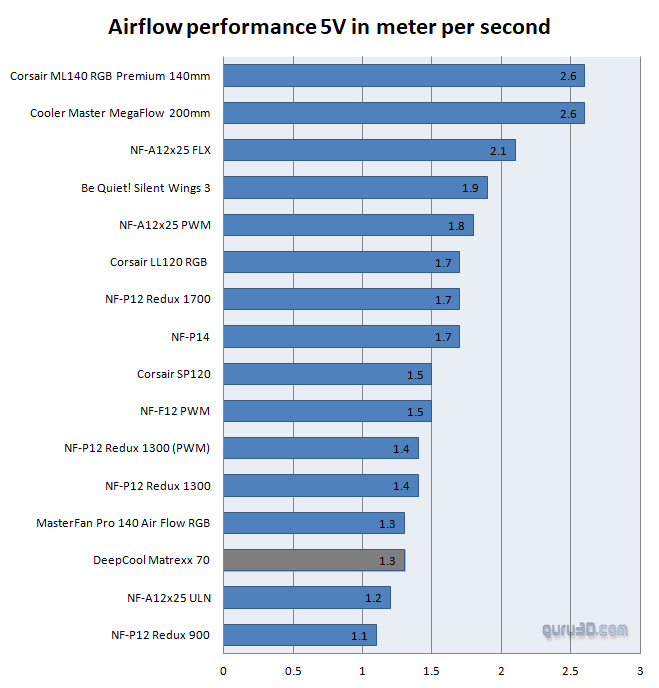
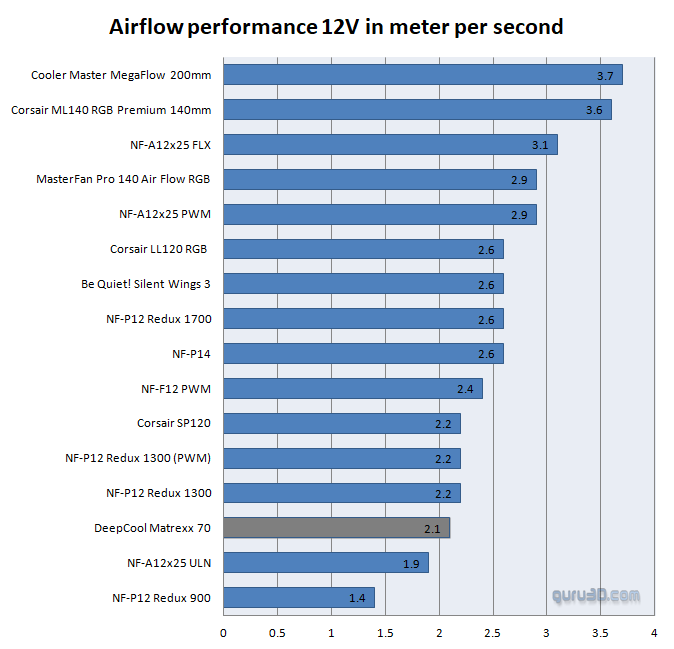
Fan airflow performance
Airflow performance
On the previous page, you have been able to see the acoustics for 5V and 12V settings. We'll now place a focus on airflow and, while a totally precise measurement, I'll classify this page as somewhat subjective. But we can get a good indication of airflow per fan at each setting.
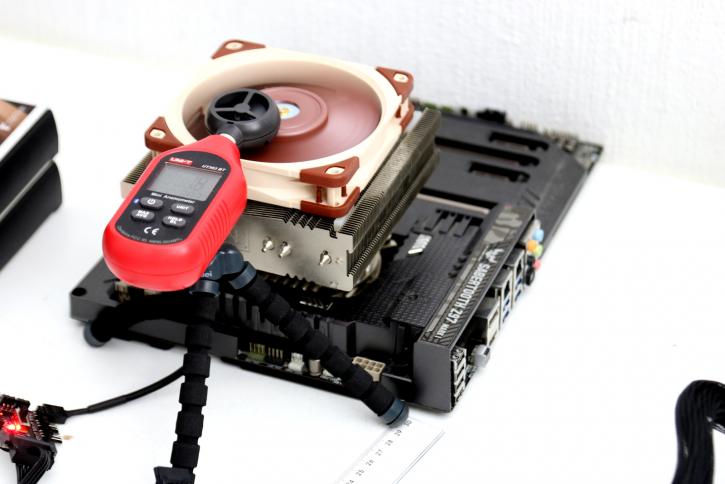
example photo of Anemometer measuring airflow
With the help of a simple to use anemometer, we can see how airflow behaves. An anemometer is a device used for measuring the speed of the wind, and actually also is a common weather station instrument. The term is derived from the Greek word anemos, which means wind, and is used to describe any wind speed instrument used in meteorology. It's a relatively cheap device to get and does seem to provide pretty steady results. Each fan is measured with the anemometer positioned precisely as shown above. Now we can measure how much air the fan is sucking inwards, the value is measured in meters per second; higher is, in this metric, better of course.
So at a 4V~5V, you're looking at average for the included fan(s). In this chart, higher is better of course. Once we fully load up the fan with 12V we can measure 2.1 meters of air being moved (wind speed) each second for the front intake fans. The fan(s) rate average for airflow.