Page 2
Radeon DNA 3 (rDNA3)
The Navi 31 GPU has made numerous appearances in leaks and rumours over the past year. This GPU is made in 5nm and has up to 12288 shader processors and 96MB of Infinity Cache. For the Radeon RX 7900 XTX, this graphics processor is stated to handle a 384-bit memory bus and capacities of up to 24GB of GDDR6 20 Gbps. AMD now touts multiple clock domains; for the XTX, that's 2.3 GHz for the shader clock frequency and 2.5 GHz for the front-end clock speed. That helps them save energy.
The company will launch its high-end series based on the Navi 31 GPU, with Navi 32 and 33 following later. AMD's next-generation RDNA 3 GPUs will use WGP (Work Group Processors) instead of CU (Compute Units). Each WGP will have two CUs, but each CU will have four SIMD32 clusters instead of just two on each CU in RDNA 2. There are also AI units present; though we lack full information, these seem to be Tensor equivalents.
The RDNA 3 architecture of the AMD Navi 31 GPU has one GCD (Graphics compute die) based on Dual SIMD units, effectively doubling up shader count. This will give 12,288 shader processors for the fully enabled GPU, also called stream processors. Compared to the 5120 SPs on the Navi 21 GPU, this is 2.4 times as many cores. The Navi 31 GPU will also have 6 MCDs (memory cache die aka infinity cache ships), each of which will have 16 MB of Infinity Cache and 64-bit (32-bit x2) memory controllers, which will give the chip a 384-bit bus interface. These are the chiplets, to one graphics die, and then infinity cache memory dies with controllers.
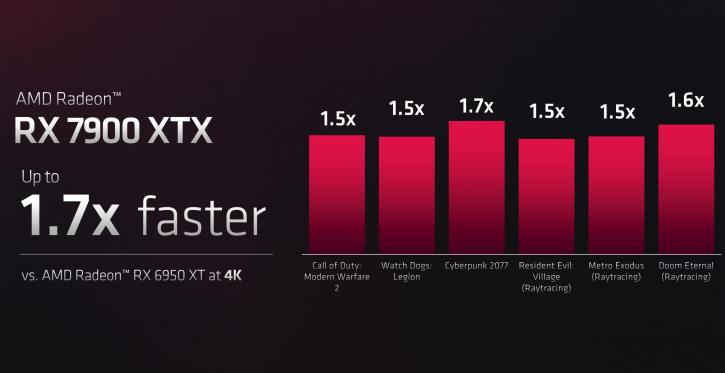
Next-generation raytracing cores should compensate for the performance that the 6000 lacked in Raytracing. Per CU, AMD claims 50% more performance.
Also update is the video or media engine, which will support AVC/HEVC simultaneous en and decode, ABV1 8k60 en/decode and AI-enhanced Video encode. on the output front, Displayport P 2.1 is supported with a display link bandwidth of up to 54 Gbps.
In its presentation, AMD also mentions HYPER-RX, a new technology to be released in Q1 next year. We're a little unclear about what it is. Still, considering the GPU-revealed AI engines, we suspect tensor-like features that increase framerates and lower latency, dubbed one-click faster framerates and lower latency. Then again, it might just be a one-click button that activates FSR and other framerate-enhancing modes.
FSR 3.0 also has been mentioned by AMD in the presentation, it'll see the light of day in 2023. Fluid Motion Frames Technology works with FSR 3.0, but the company has not said exactly what that means. We can only assume that it's something like the frame doubler that NVIDIA has implemented in DLSS 3.0.
But let's talk about the cards for a second. Next page, please.